How to check MySQL storage engine type on Linux
Last updated on November 21, 2020 by Dan Nanni
There are two major MySQL storage engines used: MyISAM and Innodb. MyISAM is non-transactional, and thus can be faster for reads, while InnoDB fully supports transactions (e.g., commit/rollback) with finer-grain locking. When you create a new MySQL table, you choose its type (i.e., storage engine). Without any choice, you will simply use a pre-configured default engine.
If you would like to know the type of an existing MySQL database table, there are a couple of ways to do it.
Method One: phpMyAdmin
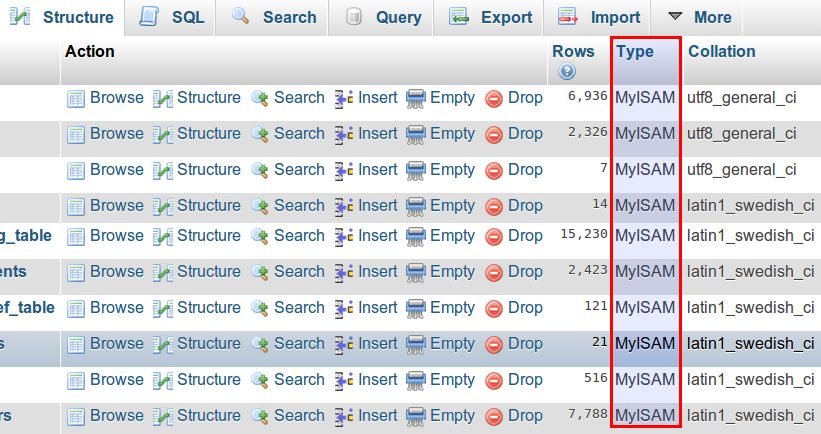
If you have access to phpMyAdmin, you can find out the database type from phpMyAdmin. Simply choose your database from phpMyAdmin to see a list of its tables. Under Type column, you will see the database type for each table.
Method Two: MySQL command line
If you can log in to a MySQL server directly, another way to identify the storage engine is to run the following MySQL command inside your MySQL server after logging in.
mysql> SELECT ENGINE FROM information_schema.TABLES WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA = 'my_database' AND TABLE_NAME = 'my_table';
The above command will show the engine type of a table called my_table in my_database database.
Method Three: mysqlshow
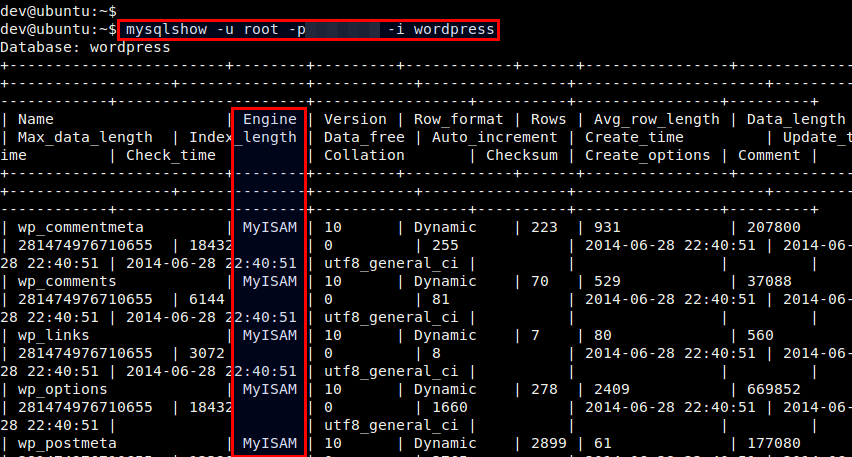
Yet another method to check the MySQL engine is to use mysqlshow, a command-line utility which shows database information. The mysqlshow utility comes with MySQL client package installation. To use mysqlshow, you need to supply MySQL server login credential.
The following command will show information about a particular database. Under Engine column, you will see the storage engine for each table.
$ mysqlshow -u <mysql_user> -p -i <database-name>
Support Xmodulo
This website is made possible by minimal ads and your gracious donation via PayPal or credit card
Please note that this article is published by Xmodulo.com under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License. If you would like to use the whole or any part of this article, you need to cite this web page at Xmodulo.com as the original source.
Xmodulo © 2021 ‒ About ‒ Write for Us ‒ Feed ‒ Powered by DigitalOcean

